
South Nahanni River is one of the key features of the Nahanni National Park Reserve it originates in the Mackenzie Mountains and changes drastically throughout its 580 km length. The section of the South Nahanni River in 1987 was proclaimed a Canadian heritage river. It was given this honour because of its recreational value and outstanding wilderness character. It is the heart of Nahanni as it is a major source to vegetation, wildlife and tourism.
Nahanni holds a variety of different ecosystems northern wilderness rivers, canyons, gorges and alpine tundra. An ecosystem in any natural wildlife area can be very delicate and requires careful management and respect, to ensure that the bio systems are not effected in a negative way. Nahanni has rules and restrictions, some yearly and some at high peak seasons, allowing the vegetation, waters and animal life to be protected from negative human effect. These sanctions, consisting of areas not allowing overnight camping to hiking in certain regions, has allowed the environment to regenerate, as well as to allow food sources for native Nahanni wildlife to regrow. These regulations have been established to protect humans from negative wildlife encounters.
Ecosystems



Virginia Falls is located on the South Nahanni River and is a waterfall that has a drop of 315 ft, this distance means that Virginia falls is twice the height of Niagra falls, masons rock is located in the center of the falls. This waterfall feeds into the rest of the water systems throughout the park.
Virginia Falls
South Nahanni River
Rabbitkettle Hotsprings
Rabbitkettle Hotsprings is the source of the largest known tufa mounds in Canada. Tufa mounds are forms of limestone that form when carbonate minerals precipitate out of ambient temperature water. These are considered to be possibly the most beautiful formations in the world of their kind.
Producers
Primary Consumer
Secondary Consumer
Tertiary
Plants that gain energy from the sun.
Herbivores that eat the plants and gain half the energy.
Carnivores that eat the Herbivores and gain half their energy.
Carnivores at the top of the chain that eat Carnivores and gain half their energy.
Trophic Levels
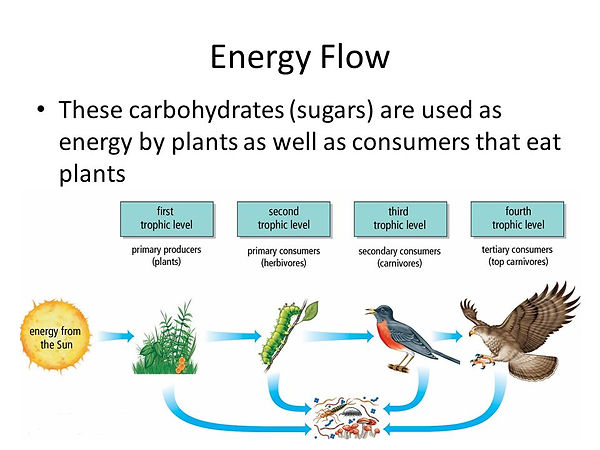
Image Credit - SlidePlayer.com
Producer
Leaves in the trees get energy from the sun (100 NRG)
Primary Consumer
A Grouse eats the leaves giving the Grouse half the energy (50 NRG) because the leaves used half the energy.
Secondary Consumer/ Tertiary
A Peregrine Falcon eats the Grouse giving the Falcon half the energy (25 NRG) because the Grouse had used half the energy
Decomposers
Worms will eat the left over parts of the flora and fauna as well as the falcons scat and gains the left over energy then the cycle starts again.
Biomagnification works similar to energy flow, except things may not go well in the end.
If some grass has pesticide on it and six Voles ate that as a source of food, the pesticide would be inside the Voles. At this point not enough to do much harm. Then three Foxes come along and eat the two Voles each. Now each Fox has double the amount of pesticide in their system. An Eagle eats the three Foxes and has six times the original amount of pesticide in it system and it kills the Eagle. The Eagle cannot handle the chemicals in its system. This can effect the ecosystem drastically. A way to identify if the ecosystem is healthy is by checking the population of Amphibians, animals like Western Toads and Leopard Frogs. These are called indicator species. Amphibians are really sensitive to things, especially changes in environment.